This project is experimental and in its very beginning stages. APIs may change significantly, and it is not yet ready for production use.
Key Features 🦆 Format Agnostic : JSON, XML, CSV, YAML, and more.
⚡ High Performance : Stream-based processing to handle large datasets efficiently.
🔄 Two-Way Mapping : Configure bidirectional mappings easily.
🔍 Schema Inference : Automatically detects schemas from sample data.
✨ Data Transformation : Apply powerful transformations on-the-fly.
🔄 Conditional Mapping : Map fields based on conditional logic.
🔗 Extensible Adapters : Plugin support for custom formats and transformations.
🐛 Rich Validation & Error Handling : Detailed validation before processing.
Getting Started Installation Basic Usage // Create a simple mapping from customer to profile val customerMapping = Platymap. flow ( "customer" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . to ( "profile" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . map ( "customer.firstName" ). to ( "profile.name.first" ). end () . map ( "customer.lastName" ). to ( "profile.name.last" ). end () . map ( "customer.email" ). to ( "profile.contact.email" ). end () . build () val jsonInput = "{ \" customer \" : { \" firstName \" : \" John \" , \" lastName \" : \" Doe \" , \" email \" : \" [email protected] \" } }" val jsonOutput = customerMapping. executeToJson (jsonInput) val xmlOutput = customerMapping. executeToXml (jsonInput) Output :{ "profile" : { "name" : { "first" : "John" , "last" : "Doe" }, "contact" : { "email" : "[email protected] " } } }
Examples Wildcard Mapping Map all fields at once from one structure to another:
val customerMapping = Platymap. flow ( "customer" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . to ( "profile" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . mapAll ( "customer.*" ). to ( "profile" ). end () . build () val jsonInput = """ { "customer": { "firstName": "John", "lastName": "Doe", "email": "[email protected] ", "age": 30, "address": { "street": "123 Main St", "city": "Anytown", "zipCode": "12345" } } } """ . trimIndent () val result = customerMapping. executeToJson (jsonInput) Flatten Nested Structures Transform nested objects into flat fields:
val addressMapping = Platymap. flow ( "customer" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . to ( "profile" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . flatten ( "customer.address" ). flattenWithPrefix ( "addr_" ). to ( "profile" ). end () . map ( "customer.firstName" ). to ( "profile.name" ). end () . map ( "customer.lastName" ). to ( "profile.surname" ). end () . build () // Create test input JSON with nested address structure val jsonInput = """ { "customer": { "firstName": "John", "lastName": "Doe", "address": { "street": "123 Main St", "city": "Anytown", "state": "CA", "zipCode": "12345", "country": "USA" } } } """ . trimIndent ()
Nest Flat Fields Group related flat fields into a structured object:
Simple1
output1
Complex example2
val productMapping = Platymap. flow ( "order" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . to ( "invoice" ) . withFormat (Format.JSON) . nest ( "order.item_*" ). asCollection ( "lineItems" ). to ( "invoice" ) . map ( "order.orderNumber" ). to ( "invoice.reference" ). end () . map ( "order.orderDate" ). to ( "invoice.date" ). end () . build () val jsonInput = """ { "order": { "orderNumber": "ORD-5678", "orderDate": "2023-05-15", "item_1_name": "Laptop", "item_1_price": 999.99, "item_1_quantity": 1, "item_2_name": "Mouse", "item_2_price": 25.50, "item_2_quantity": 2, "item_3_name": "Keyboard", "item_3_price": 75.00, "item_3_quantity": 1, "customerName": "Jane Smith" } } """ . trimIndent ()
Collection Mapping Process arrays and collections:
val orderMapping = Platymap. flow ( "order" ) . to ( "receipt" ) . map ( "orderNumber" ). to ( "receipt.reference" ). end () . map ( "customerName" ). to ( "receipt.buyer" ). end () . forEach ( "items" ). `as` ( "item" ) . create ( "receipt.lines" ) . map ( " \$ item.productName" ). to ( "description" ). end () . map ( " \$ item.quantity" ). to ( "amount" ). end () . map ( " \$ item.price" ). to ( "unitPrice" ). end () . map ( " \$ item.price * \$ item.quantity" ). to ( "total" ). end () . end () . end () . build () val jsonInput = """ { "orderNumber": "ORD-12345", "customerName": "Jane Smith", "items": [ { "productName": "Laptop", "quantity": 1, "price": 999.99 }, { "productName": "Mouse", "quantity": 2, "price": 25.50 }, { "productName": "Keyboard", "quantity": 1, "price": 75.00 } ] } """ . trimIndent () val result = orderMapping. executeToJson (jsonInput)
Conditional Mapping Apply different mapping logic based on conditions:
Mapping userMapping = Platymap . flow ( "user" ) . to ( "account" ) . branch () . when (user -> { // Check if user is admin DataNode dataNode = (DataNode) user; return "admin" . equals ( dataNode . getAsObject (). get ( "type" ). getAsString ()); }) . then () . map ( "name" ). to ( "account.adminName" ). end () . map ( "'Full Access'" ). to ( "account.permissions" ). end () . endBranch () . otherwise () . map ( "name" ). to ( "account.userName" ). end () . map ( "'Limited Access'" ). to ( "account.permissions" ). end () . endBranch () . end () . build (); Exclude sensitive fields and transform data during mapping:
Mapping userMapping = Platymap . flow ( "user" ) . withFormat ( Format . JSON ) . to ( "profile" ) . withFormat ( Format . JSON ) . mapAll ( "user.*" ) . excluding ( "user.password" , "user.ssn" , "user.creditCard" ) . transformEach ((key, value) -> { // Uppercase all string values if (value instanceof String) { return ((String) value). toUpperCase (); } return value; }) . to ( "profile.userInfo" ) . end () . build (); Architecture Platymap follows a modular architecture with:
Core Engine : Handles the mapping execution and transformation logicFormat Adapters : Convert between different data formatsFunction Registry : Manages custom transformation functionsValidation Layer : Ensures data integrity during mapping
Roadmap
Enhanced schema validation
Performance optimizations for large datasets
Additional format adapters
Visual mapping designer
Cloud integration for mapping as a service
Contributing We welcome contributions! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
License Platymap is released under the MIT License. .png)
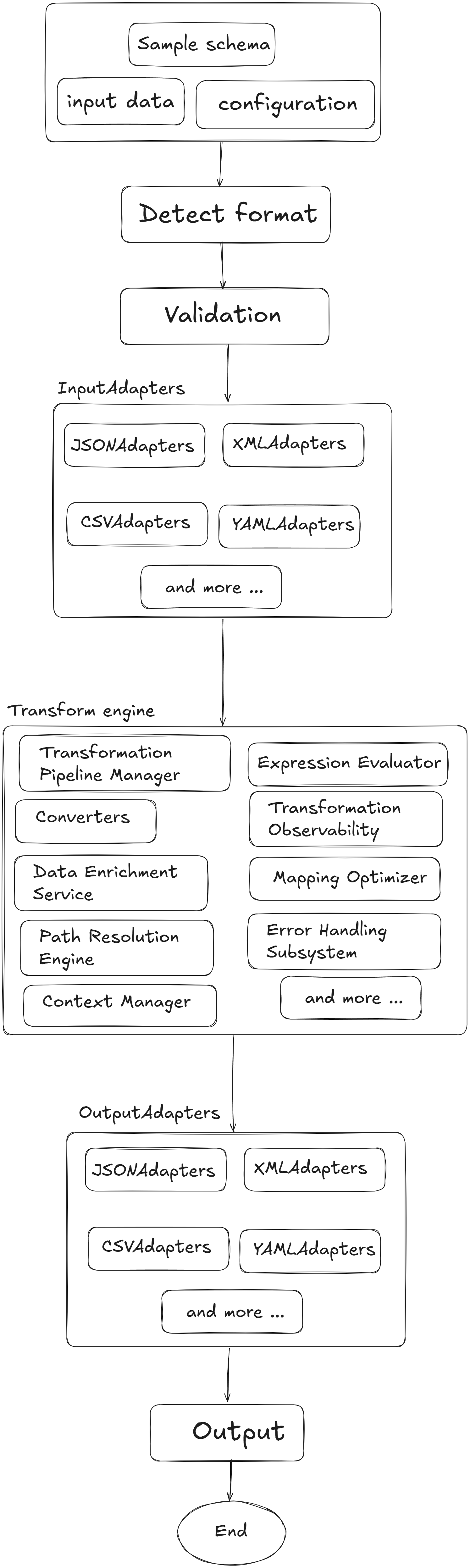 Platymap follows a modular architecture with:
Platymap follows a modular architecture with:

